Conclusion the configurational stability of a vinyl anion can be understood from the relative instability of intermediate 7 in its inversion process whereas the corresponding intermediate in the inversion of a vinyl radical 10 is relatively more stable leading to a lower energy barrier to inversion.
Why is the vinyl radical unstable.
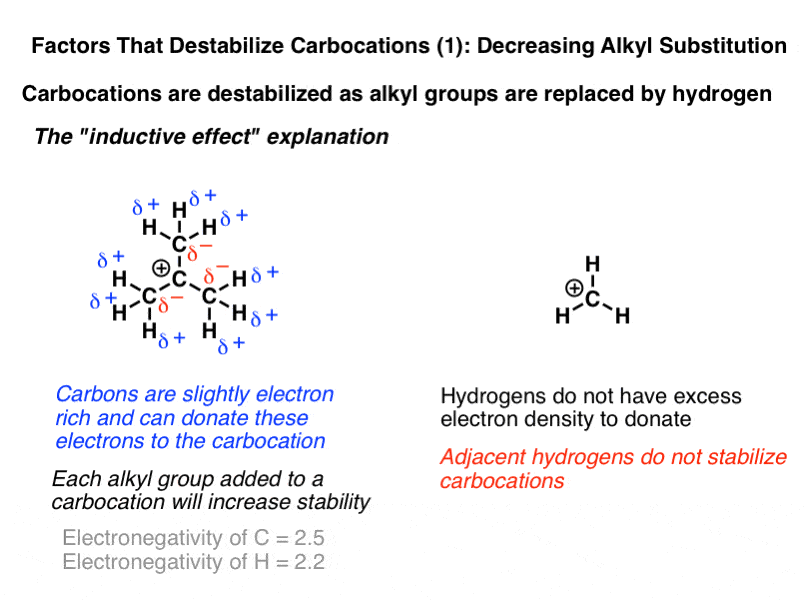
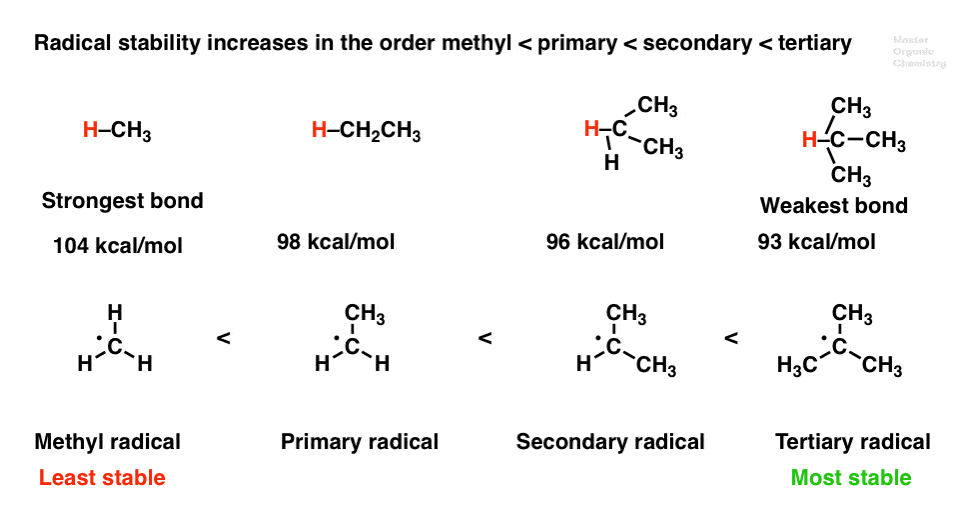
Radicals increase in stability in.
The vinyl cations are less stable due to the difference in hybridization of the carbon bearing.
The instability derives from the inability of that p orbital to overlap with the the sp2 orbitals of the carbon on the other end of the double bond.
Vinyl carbocation is unstable.
A free radical has an unpaired electron that has the highest energy among all bonding and non bonding electrons in a molecule.
Carbon with two other atoms attached prefers sp hybridization and a linear geometry.
The hybridization of a vinyl carbocation is sp hybirdized.
The instability of a vinyl cation cannot be blamed on its sp2 orbital being very electronegative as the positive charge resides in a p orbital not an sp2 orbital.
This is usually due to steric factors the reactive free radical center is surrounded by bulky groups and just not sterically accessible for reaction or electronic factors some free radicals exist in very large delocalized systems hence the spin density at any one atom in the system is so small that reaction is unlikely.
If a radical mechanism is operative in a gi ven reaction and if an alkene pi bond is present in the molecule an intramolecular radical addition reaction may be observed.
Understand the chemical and physical properties of free radicals along with the examples important uses and the sources for extracting free radicals.
When you combine the lumo of an ewg with the somo of a radical you get a lowering of the somo energy and therefore stabilisation.
What are free radicals.
A vinyl cation is a positively charged molecule a cation where the positive charge is located on a vinyl group ch ch2.