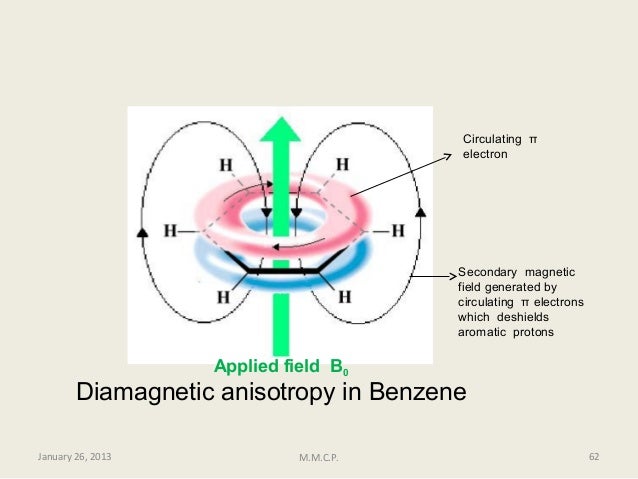
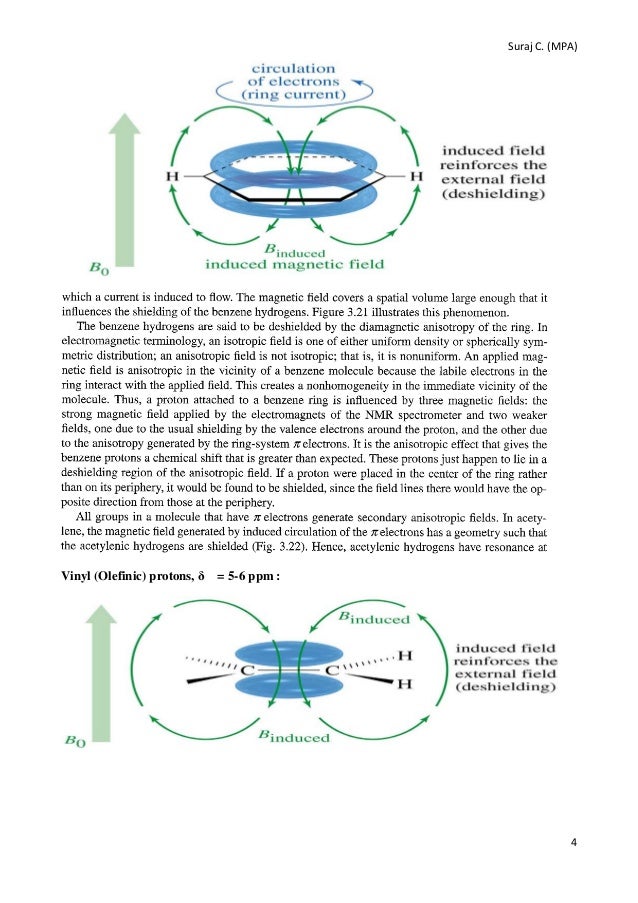
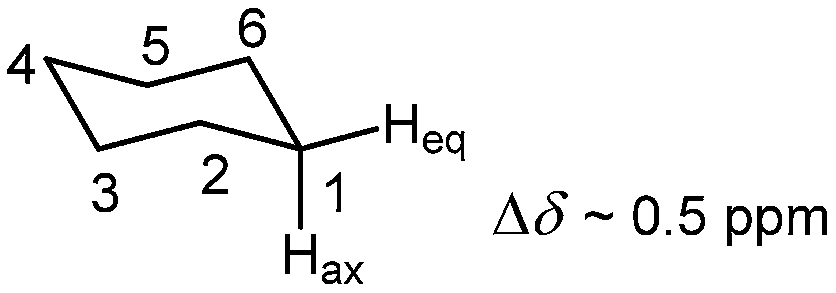Aromatics alkenes alkynes carbonyls etc interact with the applied field which induces a magnetic field that causes the anisotropy as a result the nearby protons will experience 3 fields.
Why is a vinyl proton anisotropy.
Propose possible structures for an unknown aromatic compound given its proton nmr spectrum other spectroscopic data such as a 13 c nmr or infrared spectrum or both.
You know from physics when an electron encounters a magnetic field it sticks it little right hand out and moves.
From these linear plots.
In a similar manner zeil and buchert4 examined the proton chemical shifts of a variety of acetylenes and nitriles.
Now consider 2 cyclohexenone below.
Now in the diagram consider the behaviour of the pi electrons in the applied magnetic field.
But that s not what we observed.
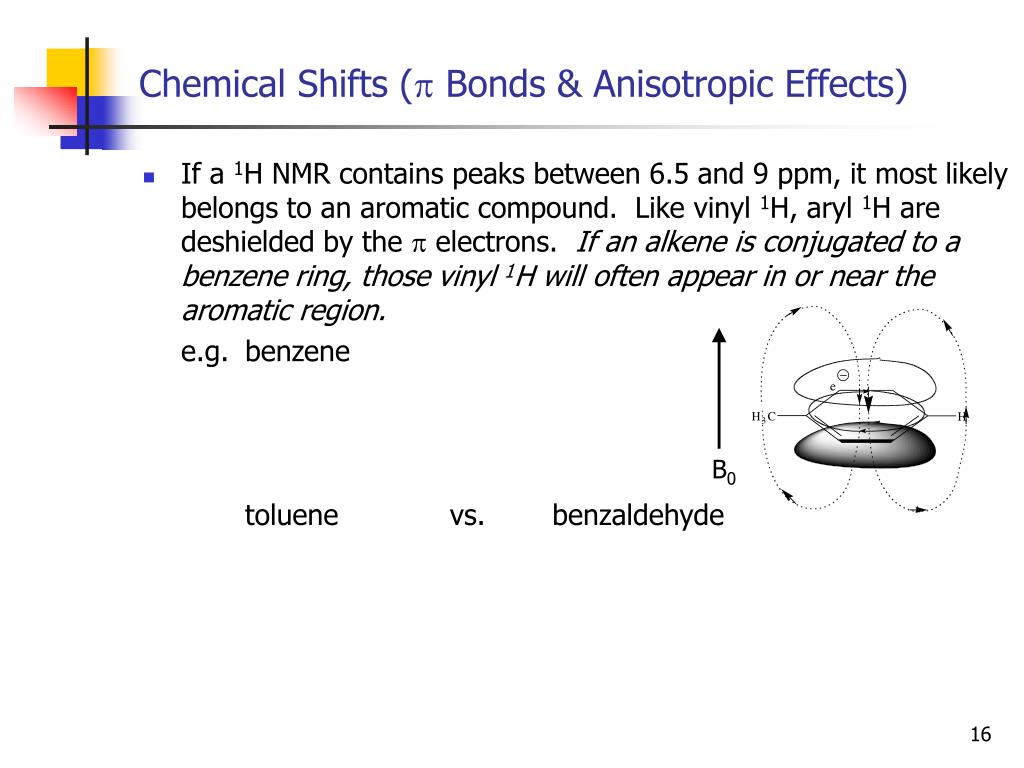
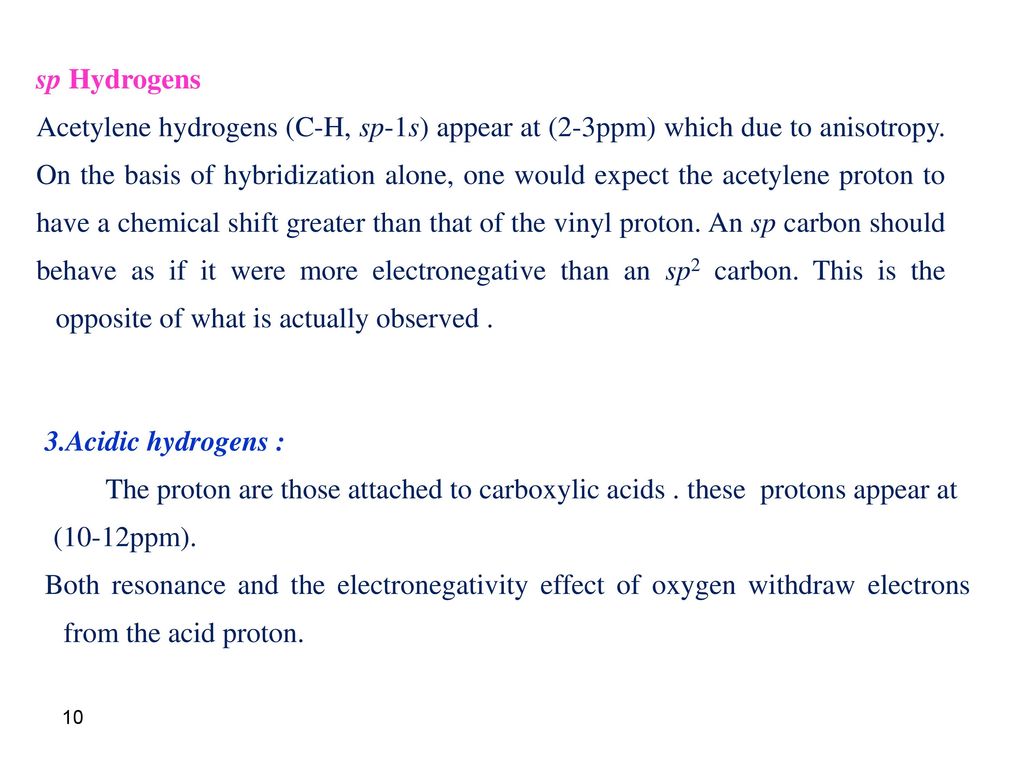
Explain why signals resulting from the presence of aryl protons are found downfield from those caused by vinylic protons in a proton nmr spectrum.
Notice that the vinyl proton closest to the electronegative oxygen is pulled downfield i e higher ppm than the one further from the oxygen.
Remember that the total population of these two spin states is roughly equal differing by only a few parts per million in a strong.
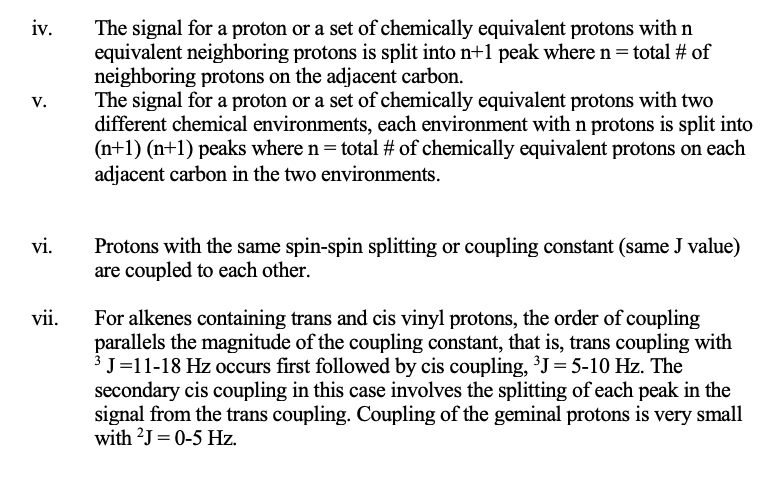
In this case a neighboring proton having a 1 2 spin shifts the resonance frequency of the proton being observed to a slightly higher value up to 7 hz and a 1 2 neighboring spin shifts it to a lower frequency.
Notice that the proton closest to the carbonyl group is at a higher chemical shift than the proton in cyclohexene 6 05 ppm for cyclohexenone vs.
The shift for this proton turns out to be approximately two to 2 5.
And let s see if we can explain why.
So if we apply an external magnetic field so b naught is our applied external magnetic field we know that causes pi electrons to.
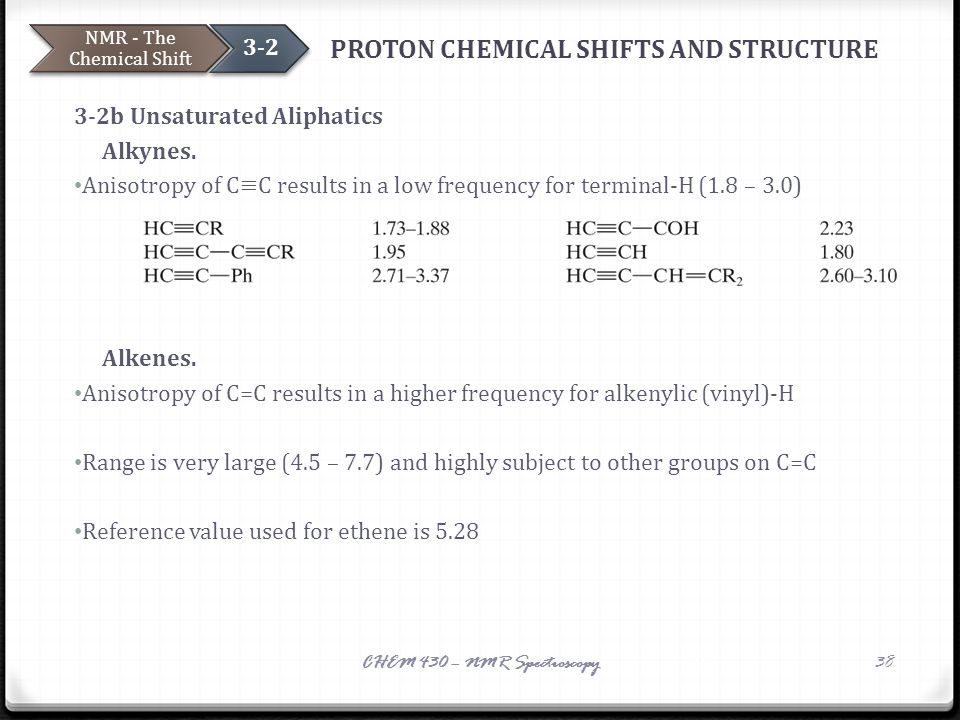
Nmr 1h chemical shifts alkenes c c anisotropy c c shielding.
The applied field the shielding.
Undergraduate students combine molecular modeling and model building with diamagnetic anisotropy to explain why the singlet for the vinyl protons in the 1h nmr spectrum of trans 1 2 dibenzoylethylene trans 1 4 diphenyl 2 butene 1 4 dione d 8 01 appears much farther downfield than that for the cis isomer d 7 14.
So it s actually a lower chemical shift than a proton on a double bond.
The word anisotropic means non uniform so magnetic anisotropy means that there is a non uniform magnetic field.
50 years but there is still controversy over the shielding effect of the double bond and no quantitative calculation of alkene proton chemical shifts has been given.
In the trans isomer the vinyl protons are found in the deshielding regions.
Assuming that the proton chemical shifts were linearly dependent on the substituent electronegativity plus a constant shift arising from the diamagnetic anisotropy gave a value of 36 x10 6.
In nmr spectroscopy possibly the best example of anisotropy occurs with the benzene molecule in which the 6 pi electrons are delocalized and free to move around the aromatic ring.
Undergraduate students combine molecular modeling and model building with diamagnetic anisotropy to explain why the singlet for the vinyl protons in the 1 h nmr spectrum of trans 1 2 dibenzoylethylene trans 1 4 diphenyl 2 butene 1 4 dione d 8 01 appears much farther downfield than that for the cis isomer d 7 14.

.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-20_00-45-54.png)









.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-21_20-55-11.png)